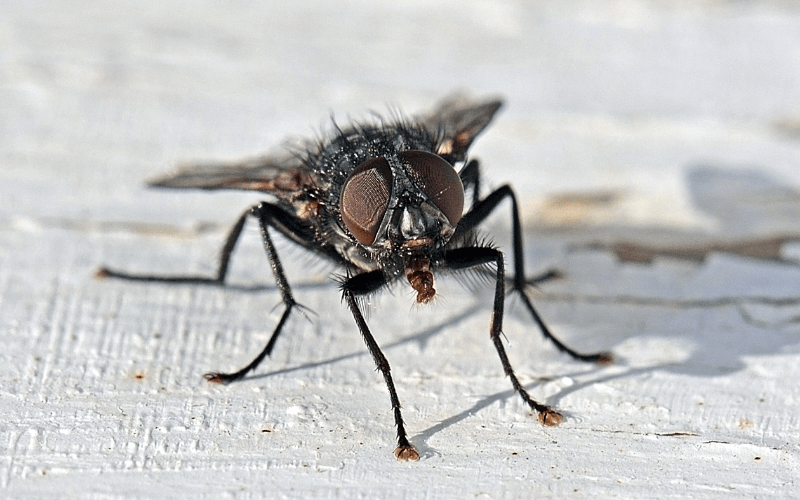
Across various regions in Spain, a surge in black fly populations has gripped attention, with experts issuing warnings about the potential health risks associated with their blood-sucking bites.
Unveiling the Black Fly
The black fly, identified by several monikers including buffalo gnat, turkey gnat, or white socks, emerges as a minuscule yet formidable insect with a penchant for blood meals. Flourishing in warm and humid climates, these creatures are especially prevalent in proximity to rivers and bodies of water.
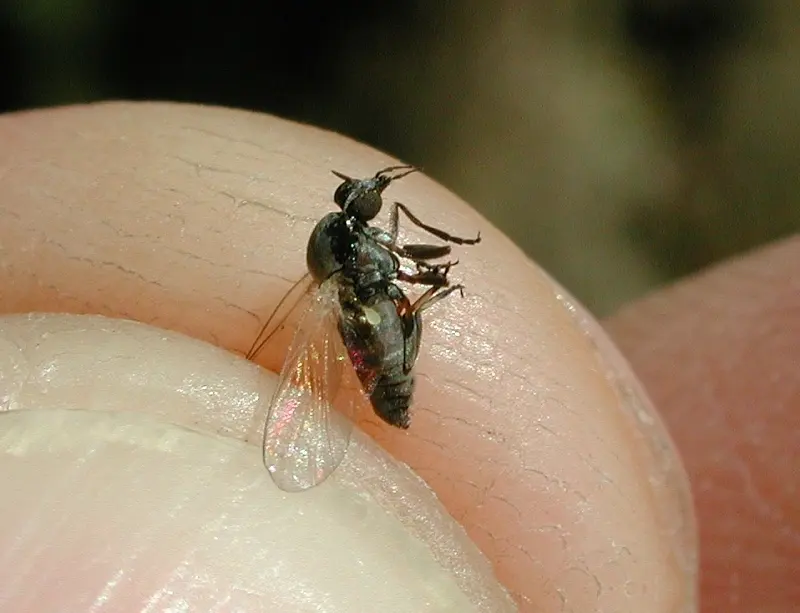

The Sting of the Black Fly Bite: Unpleasant Consequences
While the black fly bite is non-venomous, its impact can be far from benign. Inflicting a painful and irksome welt, the bite has the potential to trigger allergic reactions, infections, and in extreme cases, even lead to blindness.
Unmasking the Culprits: Factors Driving the Surge
The upswing in the black fly population is propelled by a confluence of factors, with climate change, globalization, and the dwindling bat populations at the forefront.
Climate Change: A Breeding Ground for Trouble
Climate change acts as a catalyst, rendering warmer temperatures and erratic weather patterns, which in turn foster the ideal environment for black fly breeding. These altered conditions have effectively transformed certain regions into breeding grounds for these relentless pests.
Globalization: A Pathway for Spread
Globalization plays an insidious role as well, facilitating the dispersion of black flies to new territories across the globe. Hitching rides on shipping containers and various modes of transportation, these insects venture far beyond their original habitats.
Decline of Bats: An Imbalance in Nature
The decline of bat populations has further exacerbated the issue. Bats are natural predators of black flies, and their dwindling numbers have upset the delicate balance of nature, permitting the unchecked proliferation of populations.
Navigating Black Fly Bites: Prevention Strategies
Employing preventive measures is crucial in evading black fly bites:
- Cover Up: Don long sleeves and pants when venturing into regions where black flies thrive.
- Choose Repellents: Opt for insect repellents containing DEET or picaridin.
- Thorough Application: Apply repellents diligently to exposed skin, adhering to recommended reapplication intervals.
- Strategic Timing: Avoid outdoor activities during early mornings and evenings, the prime time for black fly activity.
- Post-Bite Care: In case of a bite, cleanse the area with soap and water and soothe with a cold compress.
After the Bite: Navigating Responses
If you do fall prey to a black fly bite, taking swift action to prevent infection is imperative:
- Cleanse the Area: Gently cleanse the bite site using soap and water.
- Cool Compress: Apply a cold compress to alleviate discomfort.
- Resist Scratching: Refrain from scratching the bite, as it may exacerbate the situation.
- Medical Attention: If the bite manifests as red, swollen, or painful, or if you exhibit signs of an allergic reaction, consult a medical professional promptly.
Public Health Implications: A Graver Reality
The black fly harbors the potential to be a significant public health threat. Its bite can serve as a conduit for grave diseases such as onchocerciasis, commonly known as river blindness. This parasitic infection can cause blindness, skin lesions, and various health complications.
Additionally, there is a vector for other ailments like leishmaniasis and Chagas disease. Leishmaniasis inflicts skin ulcers, organ damage, and potentially fatal consequences. Chagas disease, another parasitic infection, manifests as heart disease, neurological afflictions, and even death.
Closing Thoughts: Vigilance and Prevention
The black fly emerges as a formidable pest with profound implications for public health. As regions grapple with surges in their populations, adopting preventive measures becomes paramount. For those planning to explore areas prone to infestations, safeguarding oneself against their bites assumes critical importance. By adhering to the aforementioned guidelines, you can contribute to curbing the risks of bites and the consequential diseases they may facilitate.